AxiGPIO¶
The AxiGPIO module provides methods to read, write, and receive interrupts from external general purpose peripherals such as LEDs, buttons, switches connected to the PL using AXI GPIO controller IP.
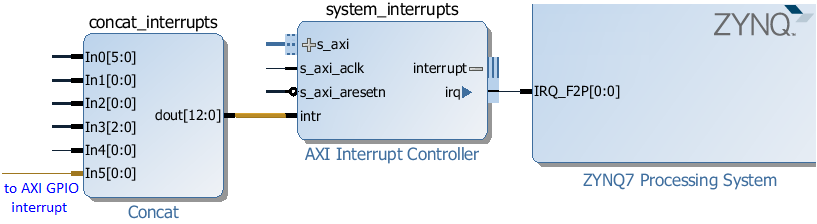
Block Diagram¶
The AxiGPIO module controls instances of the AXI GPIO controller in the PL. Each AXI GPIO can have up to two channels each with up to 32 pins.

The direction, and width of each channel can be set with the
setdirection(), and setlength() methods.
The read() and write() methods are used to read and write data.
The interrupt signal, ip2intc_irpt from the AXI GPIO can be connected directly to an AXI interrupt controller to cause interrupts in the PS. More information about AsyncIO and Interrupts can be found in the PYNQ and Asyncio section.
The LED, Switch, Button and RGBLED classes extend the AxiGPIO controller
and are customized for the corresponding peripherals. These classes
expect an AXI GPIO instance called [led|switche|button|rgbleds]_gpio
to exist in the overlay used with this class.
Examples¶
Note that this example uses the AxiGPIO instances in the base overlay directly with the AxiGPIO class. This example is for illustration, to show how to use the AxiGPIO class. In practice, the LED, Button, Switches, and RGBLED classes which extend the AxiGPIO class should be used for these peripherals.
After an overlay has been loaded, an AxiGPIO instance can be instantiated by passing the AxiGPIO name to the class.
from pynq import Overlay
ol = Overlay("base.bit")
ip_instance = ol.ip_dict['leds_gpio']
buttons = AxiGPIO(ip_instance).channel1
.. code-block:: Python
mask = 0x3 # Mask which controls which bits are written to
buttons.setdirection("out")
buttons.setlength(2)
buttons.write(0x2, mask) # Write 0x2 to the LEDs
.. code-block:: Python
ip_instance = ol.ip_dict['switches_gpio']
switches = AxiGPIO(ip_instance).channel1
switches.setdirection("in")
switches.setlength(3)
switches.read()
More information about the AxiGPIO module and the API for reading, writing and waiting for interrupts can be found in the pynq.lib.axigpio Module sections.
For more examples see the “Buttons and LEDs demonstration” notebook on the PYNQ-Z1 board at:
<Jupyter Home>/base/board/board_btns_leds.ipynb